Hunter




Information Source, please click here.
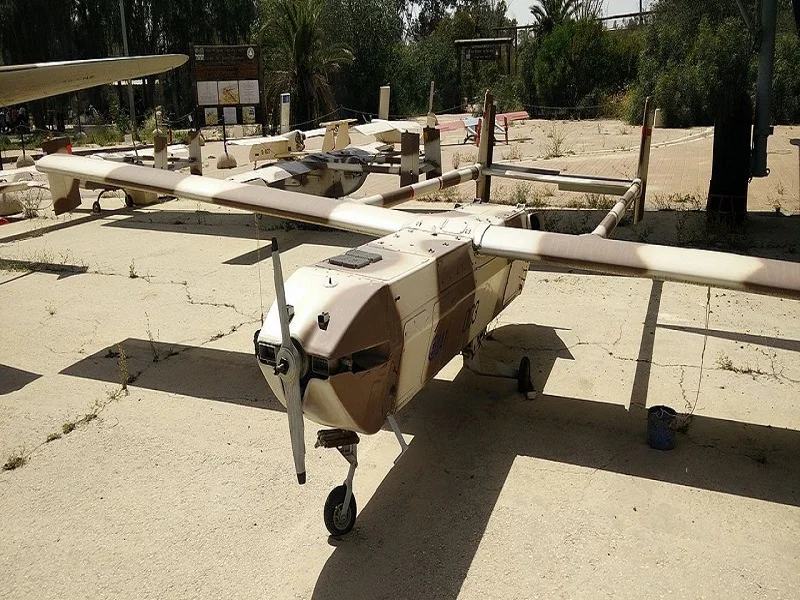
Hunter from USA, produced by Northrop Grumman
Introduce:
Hunter is a tactical unmanned aerial system (UAS) developed for the US Army. The oldest Hunter UAS of the US Army was phased out in 2015, but advanced versions of the platform are currently in service with the US Army.
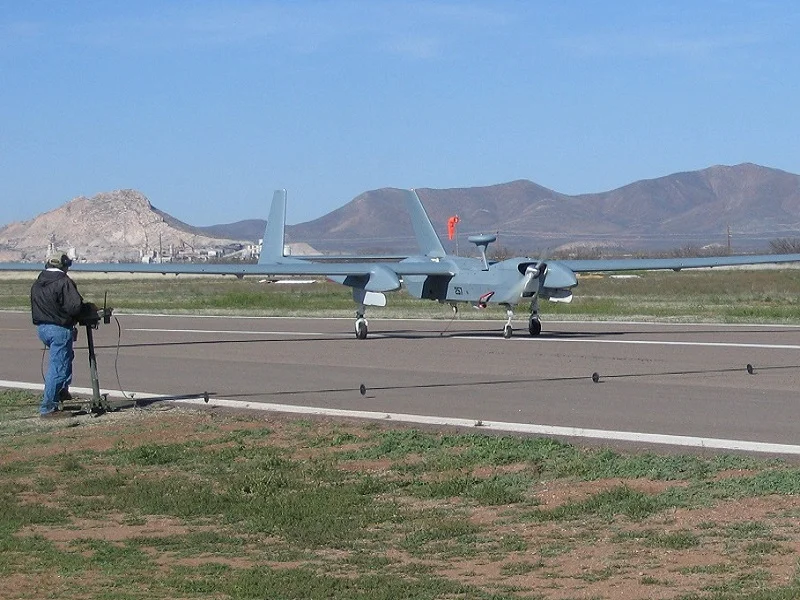
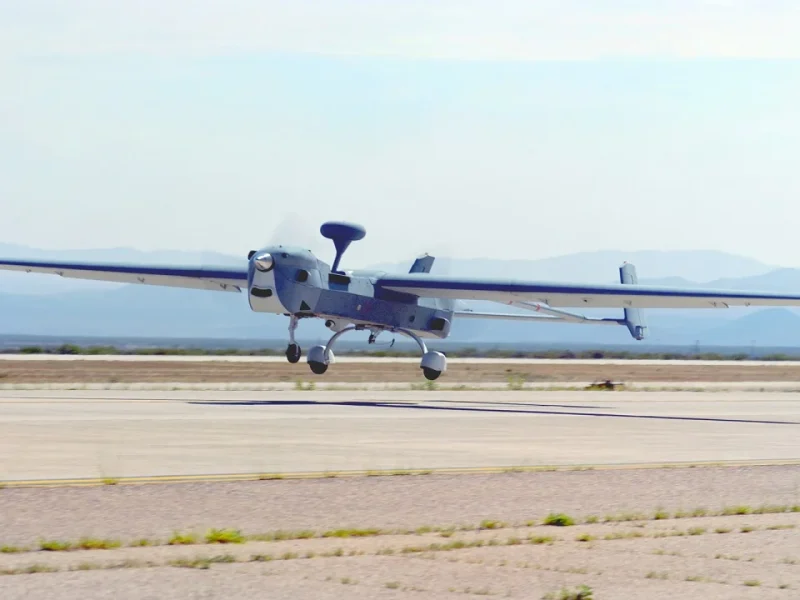
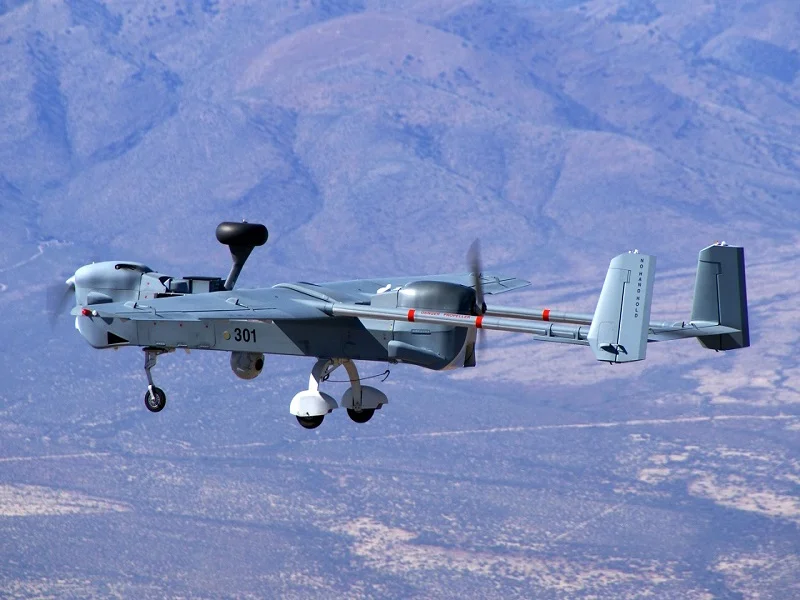
MQ-5B/C Hunter UAV
The MQ-5B Hunter has a heavy fuel engine, a ‘wet’ or fuel-carrying extended centre wing with hard points capable of weapon carriage, a new avionics suite and automated take-off and landing capability. First flight of the MQ-5B was in August 2005.
In February 2006, flight tests confirmed the MQ-5B’s endurance at more than 21 hours, which is nine hours more than the RQ-5A. The MQ-5B is fielded by the US Army in Iraq and Afghanistan and it was reported that, in September 2007, the US Army used an MQ-B Hunter deployed in Iraq to drop a laser-guide bomb on a target – the first US Army use of an armed UAV.
MQ-5C Extended Hunter (E-Hunter), a larger version of Hunter, was developed for long-endurance and high-altitude (up to 20,000ft) tactical missions. The first flight of the improved variant was conducted in April 2005. E-Hunter has a new tail assembly, and a longer centre wing which extends mission endurance to 30 hours.
In October 2002, a series of flight tests demonstrated Hunter’s ability to carry and deploy the Northrop Grumman BAT (brilliant anti-tank) submunition. The BAT submunitions destroyed a BMP combat vehicle and incapacitated a moving T-72 tank. In August 2003, Hunter successfully deployed a derivative of the BAT, the Viper Strike precision munition with semi-active laser seeker instead of infrared and acoustic sensors and 1.8kg (4lb) warhead.
RQ-5A Hunter UAV
The RQ-5A Hunter unmanned air vehicle is a fixed-wing, twin-tail boom aircraft with a dual rudder. It is propelled by two Moto-Guzzi petrol engines, each developing 60hp.
The unmanned air vehicle can be launched from a paved or semi-paved runway or it can use a rocket assisted (RATO) system, where it is launched from a zero-length launcher using a rocket booster. The RATO launch is useful on-board small ships and in areas where space is limited.
The unmanned aerial vehicle can land on a regular runway, grassy strip or highway using arresting cables.
The B-Hunter, produced by IAI for Belgium, has an automatic landing and take-off (ATLND) system. The ATLND is based on a laser tracker sensor that is used to automatically guide the air vehicle to a flare point.
The MQ-5B UAV, which is one of the top combat drones in the world, has the same fixed-wing, twin tail-boom design but with a fuel-carrying centre wing lengthened to 10.44m (34.25ft). It is powered by two ‘heavy fuel’ diesel engines developed by Northrop Grumman, one to ‘push’ and one to ‘pull’ the air vehicle. The engines allow the unmanned aircraft to operate at higher altitudes of 6,100m (20,000ft) and increase endurance from 12 hours to 15 hours.
The new avionics suite includes upgraded mission computers, a new LN-251 global positioning system / inertial navigation system (GPS/INS), an APX-118 IFF transponder and an auxiliary power distribution unit. The suite introduces a relay mode that allows one Hunter to control another at extended ranges or over terrain obstacles.
The extended centre wing has two external hard points capable of carrying weapons such as the Northrop Grumman Viper Strike laser-guided munition. The external payload is 60kg (130lb) on each wing.